What is diethylene glycol used for?
Diethylene glycol, commonly known as DEG, serves a variety of purposes, making it a versatile
compound highly valued across various industries. It functions as a humectant, natural gas
dehydrator, paper plasticiser, demulsifier, and lubricant. Moreover, it is utilized as a raw
ingredient in the production of polyester resins and plasticizers, and is widely employed in
pigments and brake fluid paste due to its remarkable softening capabilities, expected to boost the
diethylene glycol market growth. As a viscous glycol ether, it plays a crucial role as an industrial
solvent, involved in the manufacture of unsaturated polyesters, plasticizers, and significant
resins, serving as a dyeing agent for gases. DEG acts as an effective softening agent, rendering
glues and adhesives more flexible, and is an essential component in formulations of brake fluids,
pastes, and pigments.
Experience the wide-ranging applications and versatility of Diethylene Glycol with Boxa Chemical
Co.,Limited。 Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and unlock the possibilities
offered by this valuable compound. Additionally, Diethylene glycol serves as a solvent in the
chemical industry, dissolving resins, paints, coatings, inks, adhesives, and more. It is commonly
utilized as a component in automotive antifreeze due to its low toxicity and excellent antifreeze
properties. Moreover, it can enhance the performance of lubricating oils and reduce frictional
losses as a lubricant. Diethylene glycol also acts as a plasticizer for plastics, improving their
flexibility and ductility, and finds applications in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent or
diluent for drugs. In cosmetics, such as skincare products, perfumes, and lipsticks, Diethylene
glycol is employed as a solvent and diluent.
How is diethylene glycol made?
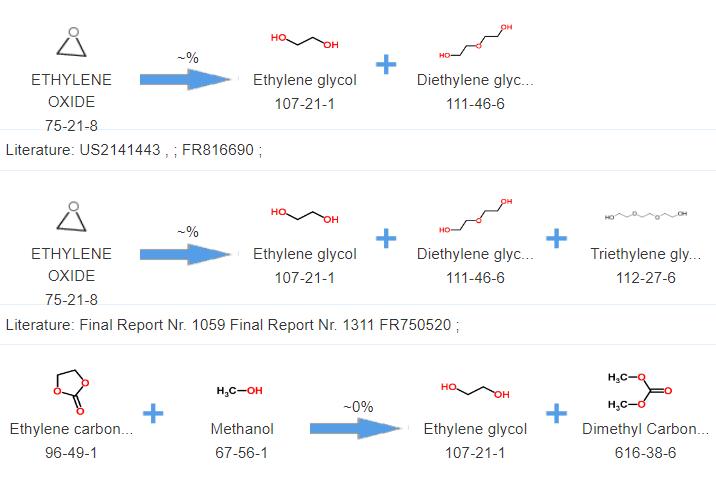
Diethylene glycol is typically produced through the partial hydrolysis of ethylene oxide. This
reaction results in the formation of monoethylene glycol (MEG) and diethylene glycol as co-products.
Diethylene glycol can then be separated from the reaction mixture through processes such as
distillation or fractional crystallization. Additionally, diethylene glycol can also be obtained as
a byproduct in the production of ethylene glycol.
Is diethylene glycol hazardous ?
Diethylene glycol can be hazardous if not handled properly. It is classified as a toxic substance
and can pose health risks if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. Ingestion of
diethylene glycol can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and in severe
cases, kidney and liver damage. Inhalation of its vapors can irritate the respiratory tract and
cause symptoms such as coughing and shortness of breath. Skin contact with diethylene glycol may
result in irritation or allergic reactions.
Moreover, diethylene glycol is flammable and can pose fire hazards under certain conditions.
Therefore, appropriate safety measures should be taken when handling diethylene glycol, including
wearing protective equipment, ensuring adequate ventilation, and implementing proper storage and
disposal procedures.
What are the differences between Diethylene Glycol and Ethylene Glycol
Chemical Structure: The chemical structure of Diethylene Glycol is HOCH2CH2OCH2CH2OH, whereas
Ethylene Glycol has the chemical structure HOCH2CH2OH.
Physical Properties: Diethylene Glycol is a viscous liquid, while Ethylene Glycol is a colorless
liquid. Additionally, Diethylene Glycol is more odorous compared to Ethylene Glycol.
Applications: Diethylene Glycol and Ethylene Glycol each have their own industrial and commercial
applications. Ethylene Glycol is commonly used as a solvent, coolant, and antifreeze, while
Diethylene Glycol finds applications in pharmaceuticals, paints, coatings, and cosmetics.